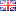
Hair grows in naturally occurring groups of 1-4 hair, called Follicular Units.
Single follicular units are allocated along the frontal hairline and as we move towards the back of the scalp, hair follicles constitute groups of up to 4 hairs.
Follicular units are complete biological units that comprise nerves, blood vessels, sebaceous glands, collagen and the small muscle arrectorpili.
Each follicular unit has a predetermined genetic definition.
In cases of female hair loss, the hair follicles on the front and top of the scalp are susceptible to the hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT), derivative of testosterone.
The Role of the Hormones
Testosterone, with the help of the enzyme 5-a reductase is converted into DHT, which acts on hair follicles receptors and leads to their miniaturization.
The prolonged action of Androgens to the vulnerable follicles makes them produce hairs that gradually shrink and finally fall out.
Female hair loss mechanism is similar but more complicated than that of male hair loss, as it involves the 2 steroid-metabolizing enzymes 5-a reductase and aromatase.
5a-reductase converts testosterone into DHT and aromatase converts and rostenedione to estrone and estradiol. That means that aromatase has a protective role in hair loss as it discourages the formation of DHT.
Female pattern hair loss affects women having high hormonal levels or normal hormonal levels in combination with hereditary predisposition.
Women have lower levels of testosterone and 5-a reductase in their bodies, and thus create smaller quantities of DHT, which is responsible for hair follicles shrinking.
Moreover, the female organism has higher levels of aromatase -which suppresses the severity of hair loss; there is 50% more aromatase in the frontal area of a woman΄s scalp than in other parts of her scalp.
Effect on Women
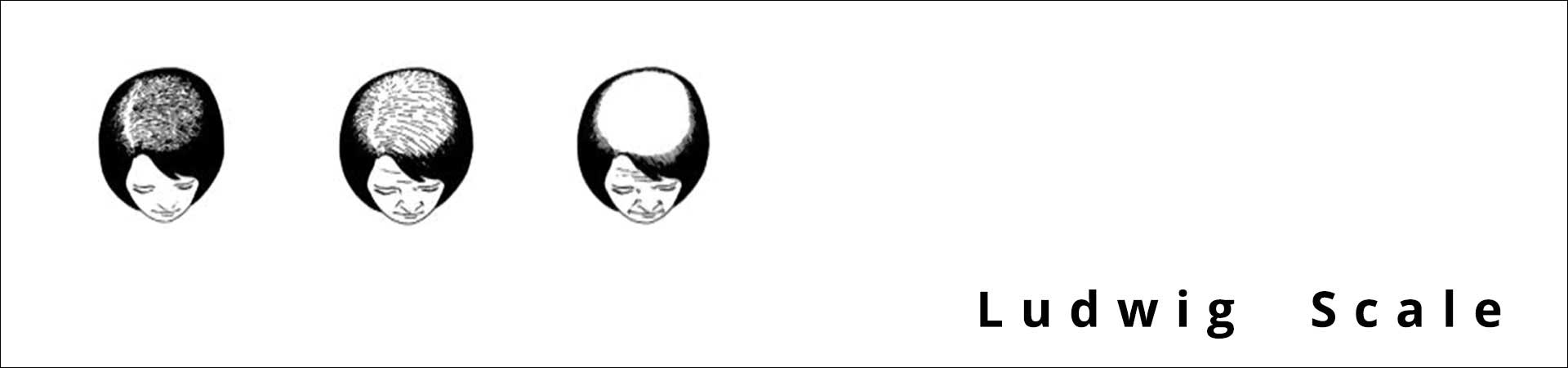
This mechanism of function illustrates the different hair loss patterns between men and women, as well as the limited effectiveness of medicines that block DHT formation in women: women usually experience diffuse hair loss with emphasis on the upper area of the scalp, while at the same time preserve the frontal line.
Female pattern hair loss is clinically represented by the Ludwig Classification.
Other Types of Hair Loss
- Telogen Effluvium
- Anagen Effluvium
- Alopecia Areata
- Male – patterned hair loss
- Trichotillomania
- Traction alopecia
- Alopecia caused by trauma